Users with experience in the field of IT and security she's quite used to coming across highly technical terms that other people wouldn't know how to define. Today we will talk about the DMZ and we will explain what it is for and how to activate it.
Today, computer networks are an essential part of any business environment and, in terms of security, it must be as effective as possible if we want security to reign in the work environment. One of the functions of the router is to block network ingress ports to keep it safe from external connections. Here we talk about the DMZ.
Before explaining what the DMZ is and what it is for, we want to highlight a very important factor. In any type of action that implies the words security and informatics, We must be very cautious and always carry out these configurations if we have the necessary knowledge or have professional support. With that said, let's see what the DMZ is.
What is the DMZ?
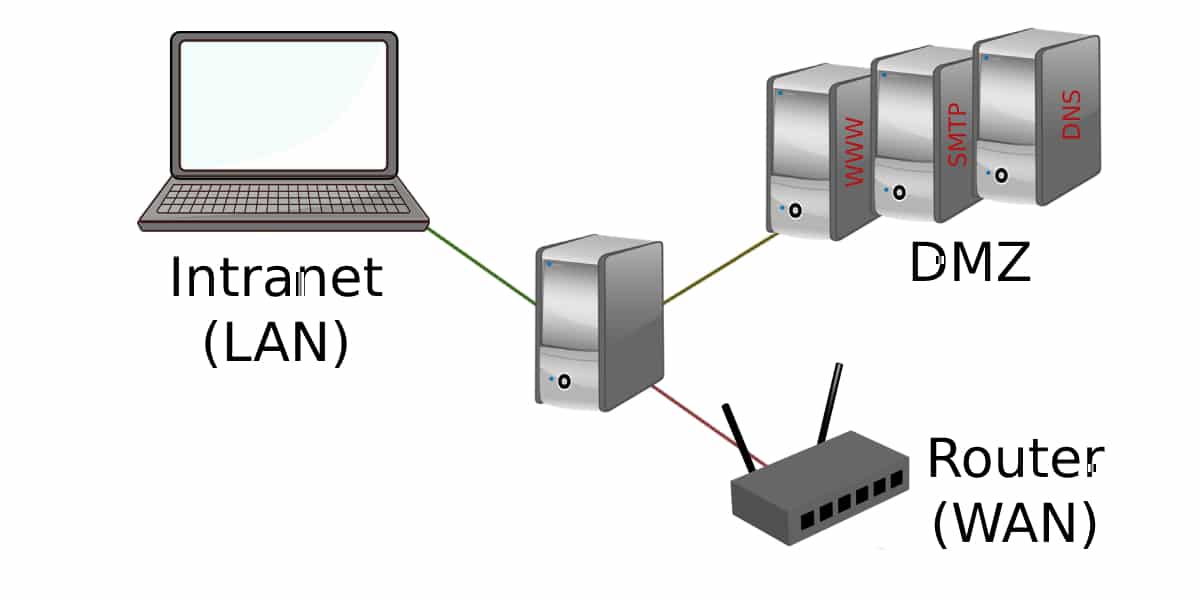
The DMZ or “Demilitarized Zone” is a mechanism commonly used in the business environment to protect network connections. It is a local network (private IP) that is located between the internal network of any company and the external network to it (Internet).
A demilitarized zone is an isolated network found within the internal network of a company or organization. That is, the DMZ It acts as a filter between the internet connection and the network of private computers where it is operating. Thus, the main objective is to verify that the connections between both networks are allowed.
In this network are located those files and resources of the organization that must be accessible from the internet (email servers, file server, CRM applications, DNS or ERP servers, web pages, etc.). Therefore, the DMZ establishes a "security zone" of several computers that are connected to the network.
What is?

The DMZ has the main function of allowing computers or Hosts to provide services to the external network (Email) and function as a protective filter for the internal network, acting as a "firewall" and protecting it from malicious intrusions that could compromise security.
DMZs are commonly used to locate the computers to be used as servers, which must be accessed by external connections. These connections can be controlled using Port Address Translation (PAT).
The DMZ, as we have said, is often used in business environments, but can also be used in small office or home. The DMZ can be used to perform firewall tests on a personal computer or because we want to change the router provided by the company.
Activating the DMZ of a router can be very useful in case of not being able to connect remotely from outside our network. Lets see what the failure is if we do not know if we have a port problem, an application configuration or a DDNS failure.
What is the typical configuration of the DMZ?
DMZs are usually configured with two Firewall, adding a security plus to the network they protect. In general, they are usually placed between a firewall that protects from external connections and another firewall, found the entry of the internal network or subnet firewall.
Ultimately, DMZs are important network security features designed to keep data safe and prevent unwanted intrusions.
How to configure the DMZ?

In order to configure the DMZ, the user must implement a Determined and unique IP for the computer that needs the service. This step is essential so that this IP is not lost and that it is destined to another computer. Then the following steps should be followed:
- Enter the menu DMZ configuration (Located on the router. You can try looking for it in your router's guide). We can also find this in the area of "Advanced port configuration".
- We will select the option that allows us access IP address.
- Here we will remove Firewall that we want to withdraw.
Advantages and disadvantages of configuring the DMZ

Advantages
In general, configuring the DMZ provides greater security in terms of computer security, but it should be noted that the process is complex and should only be done by a user who has the necessary knowledge of network security.
Generally, users configure the DMZ to optimize the performance of applications, programs, video games or web and online services. For example, enabling the DMZ is beneficial for play with consoles, on many occasions we need this functionality precisely to play online correctly and not have problems with Moderate NAT and open ports.
DMZ configuration allows disable services that are not being used for prevent other people from reaching the information that contain the equipment that are interconnected to the network.
Disadvantages
Setting up the DMZ is something that not everyone knows how to do, so doing it the wrong way can lead to the possibility of lose or suffer from some kind of copy in all the information that the system has. Therefore, it will be strictly necessary that only those who are totally sure of what they are doing carry out this action.
Generally speaking, setting up the DMZ is very beneficial for those business environments in which it is very necessary to provide the greatest fullfilment of security requirements in concept of network connections. Therefore, you must have IT professionals who correctly configure the DMZ.
Otherwise, if the DMZ confirmation is not carried out neatly and in detail, it can be very dangerous and may lead to loss of information of our team or attract malicious external intrusions. We recommend that you have professional computer security support if you are thinking of dealing with this issue.
And you, have you configured the DMZ of your router? Let us know in the comments.