
With each new version of Windows, Microsoft does everything possible so that users adopt it quickly with a series of tools that we allow you to go back to the previous version of Windows in a very simple way without losing the information and / or applications that we had in the previous version.
With Windows 10, when updating from a previous version (Windows 7 or Windows 8.x), we have the option during the installation of keep the previous copy in case we want to go back. Although we do not select that option, Microsoft wants to cure itself in health and still, it makes a backup of the previous version of Windows.
What is windows.old
As I have commented in the previous paragraph, it does not matter if during the installation we select that we do not want to keep a backup copy of the current version of Windows, since automatically, a copy of the entire system is made, which allows us to restore it again as if we had not installed a new version.
Where is this copy of the previous version of Windows stored? In the windows.old folder. The windows.old folder, that folder that occupies several gigs and that we cannot delete in any way, is where all the files corresponding to the previous version of Windows are stored.
Where the windows.old folder is located
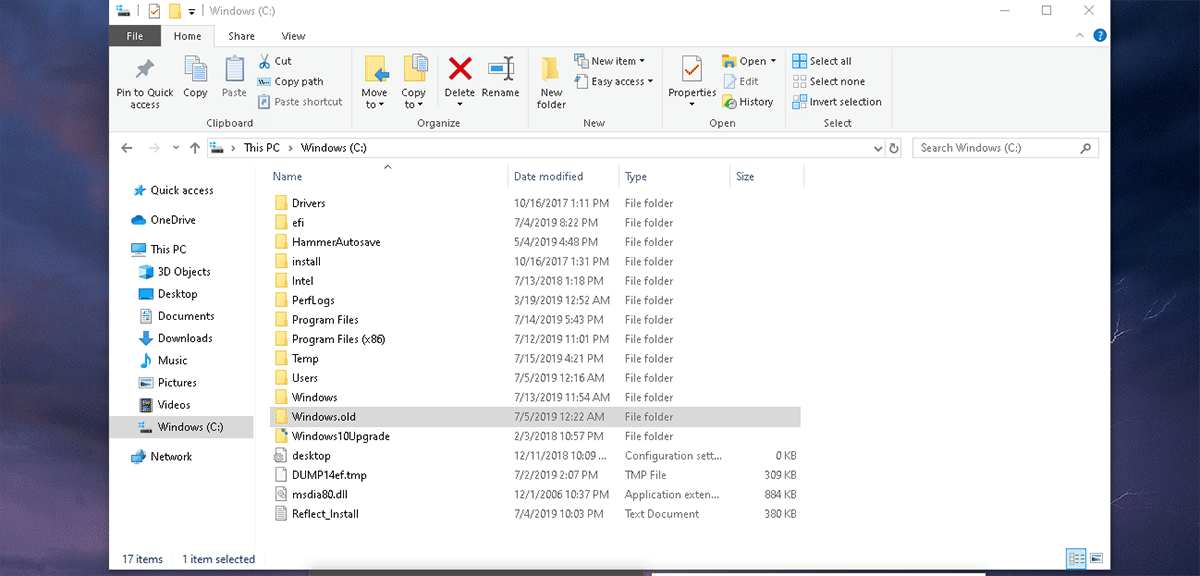
The windows.old folder is located in the system root directory, on the main unit of the computer where it is installed (which in most cases is C). Inside we find a series of files that we can only access if we restore that version through the Windows configuration options.
This folder is protected and we can't send it to the Recycle Bin. This is because it requires the permissions of that account, that is, of the Windows user of that version. Although we know the credentials, we do not have the opportunity to enter them anywhere to unlock access.
What happens if I delete the files from the windows.old folder
Nothing. Absolutely nothing happensWell, yes, we are not going to be able to restore the previous version of Windows that our computer was running before the installation of the new version / update. If we are short of space on our hard drive (this folder usually occupies about 20 GB on average).
Microsoft has natively established a trial period of 30 days, after which it understands that the user has adapted the new version of Windows and does not intend to return to the previous version, so it proceeds to delete it automatically.
How to delete the windows.old folder
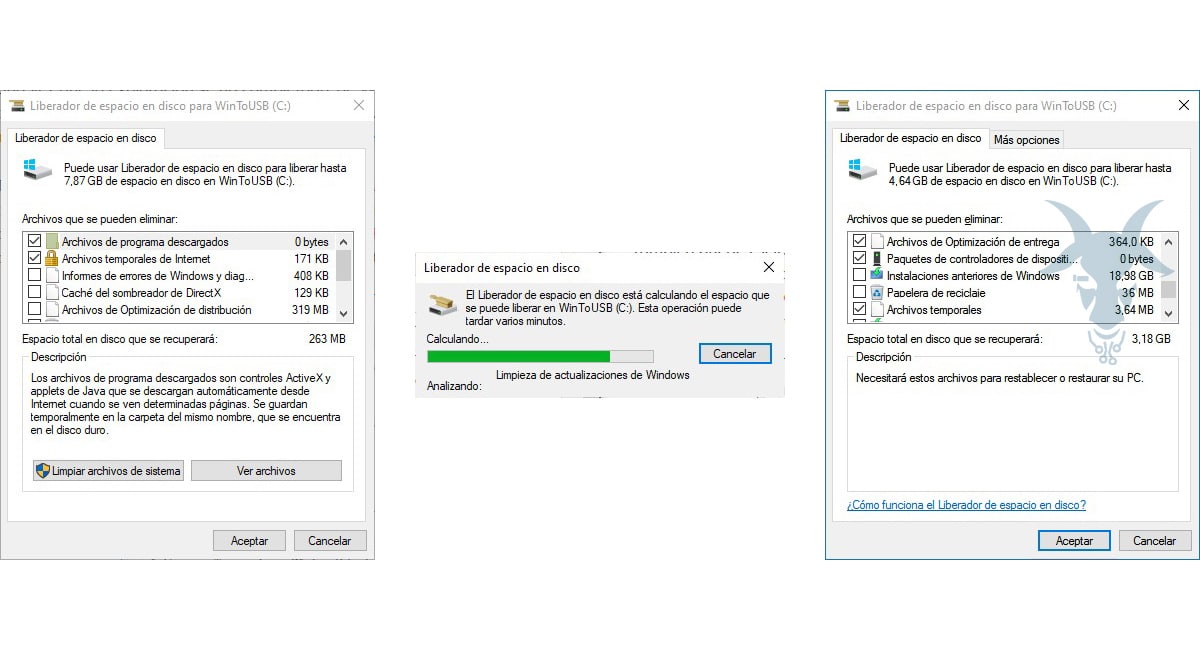
The simplest way to be able to erase both the windows.old folder and all its contents and to be able to use the large amount of space it occupies on our computer, we can only perform this operation in one way, and that is through the Disk Cleanup application
This application is available natively and we can find it quickly by writing its name in the Cortana search box located just to the right of the Windows Start button.
- As they are system files, we must access the advanced properties of the application through the button Clean up system files.
- Inside the System Files menu, we look for the box with the name Previous Windows installations and we mark it. Through this option, we can also delete the files of the updates that have been installed recently.
- Once we have marked the boxes of all the options that we want to eliminate, we must click on the OK button and wait for the process to finish.
Depending on the size of the windows.old folder and the type of hard drive that we have in our computer (HDD or SSD), the process can last from a few minutes (in the case of HDD) up to just a few seconds (in the case of an SSD).
Once we have deleted the windows.old folder, it is advisable to restart our computer so that Windows completely forget about installation that we previously had stored in our computer and space.
This is the easiest method to delete the contents and the windows.old folder, but there is another way, a form that requires certain knowledge of DOS, although if you follow the steps detailed below, you can eliminate it without problems.

- The first thing we must do is access the system through the CMD command (type in the search box to access the command prompt).
- To have full access to the folder we want to delete we write: takeown / F c: \ Windows.old \ * / R / A
- To obtain the same permissions as the user of the account we want to delete, we write: cacls c: \ Windows.old \ *. * / T / grant administrators: F
- Through the command: rmdir / S / Q c: \ Windows.old we remove both the directory and all its content.
I need more space How to free up space in Windows 10?
Not only does the windows.old folder occupy a large amount of space on our hard drive, but we must also take into account the system updates, some updates that can also occupy a large amount of space on our hard drive.
To eliminate the updates already installed on our computer without waiting for them to be automatically deleted when the system considers it, we must make use of the native application Disk Cleanup (We can access it through the search engine located to the right of the Windows Start button).
To access the system updates and be able to delete them, we must click on the button Clean system files. We wait a few seconds and then the system files will be displayed, including system updates, which we can delete to free up space on our hard drive.
We check the box Windows update cleanup, along with the rest of the available options if we want to free up more space and click on OK. This process will last a few seconds and will allow us to obtain a valuable space that was being occupied by Windows 10 for no reason, since the updates are already installed on the computer.
If we plan to upgrade our computer to Windows 10, the best we can do is download the latest ISO available from the Microsoft website, since this ISO includes all updates that have been released from the system, so once installed, you won't have to wait several hours to download the latest updates and then delete them.
Another solution to free up space in Windows 10 is to use an external hard drive to not only backup Windows 10, without also to be able store content that we do not plan to use daily on our computer, such as images, movies, videos, applications ...
